|
|
|---|
Wednesday, October 6, 2010
Flowers and it's collection
For other uses, see Flower (disambiguation).

A poster with twelve species of flowers or clusters of flowers of different families
In addition to serving as the reproductive organs of flowering plants, flowers have long been admired and used by humans, mainly to beautify their environment but also as a source of food.
Flower specialization and pollination-
Further information: Pollination syndrome

Callistemon citrinus flowers
Cleistogamous flowers are self pollinated, after which they may or may not open. Many Viola and some Salvia species are known to have these types of flowers.
The flowers of plants that make use of biotic pollen vectors commonly have glands called nectaries that act as an incentive for animals to visit the flower. Some flowers have patterns, called nectar guides, that show pollinators where to look for nectar. Flowers also attract pollinators by scent and color. Still other flowers use mimicry to attract pollinators. Some species of orchids, for example, produce flowers resembling female bees in color, shape, and scent. Flowers are also specialized in shape and have an arrangement of the stamens that ensures that pollen grains are transferred to the bodies of the pollinator when it lands in search of its attractant (such as nectar, pollen, or a mate). In pursuing this attractant from many flowers of the same species, the pollinator transfers pollen to the stigmas—arranged with equally pointed precision—of all of the flowers it visits.
Anemophilous flowers use the wind to move pollen from one flower to the next. Examples include grasses, birch trees, ragweed and maples. They have no need to attract pollinators and therefore tend not to be "showy" flowers. Male and female reproductive organs are generally found in separate flowers, the male flowers having a number of long filaments terminating in exposed stamens, and the female flowers having long, feather-like stigmas. Whereas the pollen of animal-pollinated flowers tends to be large-grained, sticky, and rich in protein (another "reward" for pollinators), anemophilous flower pollen is usually small-grained, very light, and of little nutritional value to animals.
Attraction methods-

A Bee orchid has evolved over many generations to better mimic a female bee to attract male bees as pollinators.
Still other flowers use mimicry to attract pollinators. Some species of orchids, for example, produce flowers resembling female bees in color, shape, and scent. Male bees move from one such flower to another in search of a mate.
Fertilization and dispersal
Main article: biological dispersal

Cassia Fistula. A hermaphrodite flower showing both male and female parts.
The general assumption is that the function of flowers, from the start, was to involve other animals in the reproduction process. Pollen can be scattered without bright colors and obvious shapes, which would therefore be a liability, using the plant's resources, unless they provide some other benefit. One proposed reason for the sudden, fully developed appearance of flowers is that they evolved in an isolated setting like an island, or chain of islands, where the plants bearing them were able to develop a highly specialized relationship with some specific animal (a wasp, for example), the way many island species develop today. This symbiotic relationship, with a hypothetical wasp bearing pollen from one plant to another much the way fig wasps do today, could have eventually resulted in both the plant(s) and their partners developing a high degree of specialization. Island genetics is believed to be a common source of speciation, especially when it comes to radical adaptations which seem to have required inferior transitional forms. Note that the wasp example is not incidental; bees, apparently evolved specifically for symbiotic plant relationships, are descended from wasps.
Usage-

Flower market, Detroit's Eastern Market.
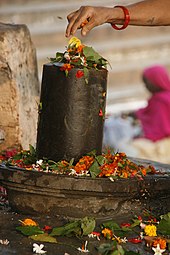
Female hand spreading flowers over a Lingam temple in Varanasi
- For new births or Christenings
- As a corsage or boutonniere to be worn at social functions or for holidays
- As tokens of love or esteem
- For wedding flowers for the bridal party, and decorations for the hall
- As brightening decorations within the home
- As a gift of remembrance for bon voyage parties, welcome home parties, and "thinking of you" gifts
- For funeral flowers and expressions of sympathy for the grieving
- For worshiping goddesses. in Hindu culture it is very common to bring flowers as a gift to temples.
Flowers provide less food than other major plants parts (seeds, fruits, roots, stems and leaves) but they provide several important foods and spices. Flower vegetables include broccoli, cauliflower and artichoke. The most expensive spice, saffron, consists of dried stigmas of a crocus. Other flower spices are cloves and capers. Hops flowers are used to flavor beer. Marigold flowers are fed to chickens to give their egg yolks a golden yellow color, which consumers find more desirable. Dandelion flowers are often made into wine. Bee Pollen, pollen collected from bees, is considered a health food by some people. Honey consists of bee-processed flower nectar and is often named for the type of flower, e.g. orange blossom honey, clover honey and tupelo honey.
Flower delivery network using florists across the nation who hand-deliver flowers, bouquets and arrangements. International delivery also offered.
Order flowers, roses, gift baskets and more. Get same-day flower delivery for birthdays, anniversaries, and all other occasions. Find fresh flowers at ..
Over 20000 online pictures of flowers and garden pics with free flower wallpapers and flower backgrounds. Names of many different types of flowering garden ...
When selecting plants, choose those with white or pastel flowers and light or variegated foliage. Light colors will stand out in the shade, ...
From Wikipedia-
Labels: florida news, picture and vedio also.
0 Comments:
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)















